Table of Contents
Common Symptoms of Psoriasis
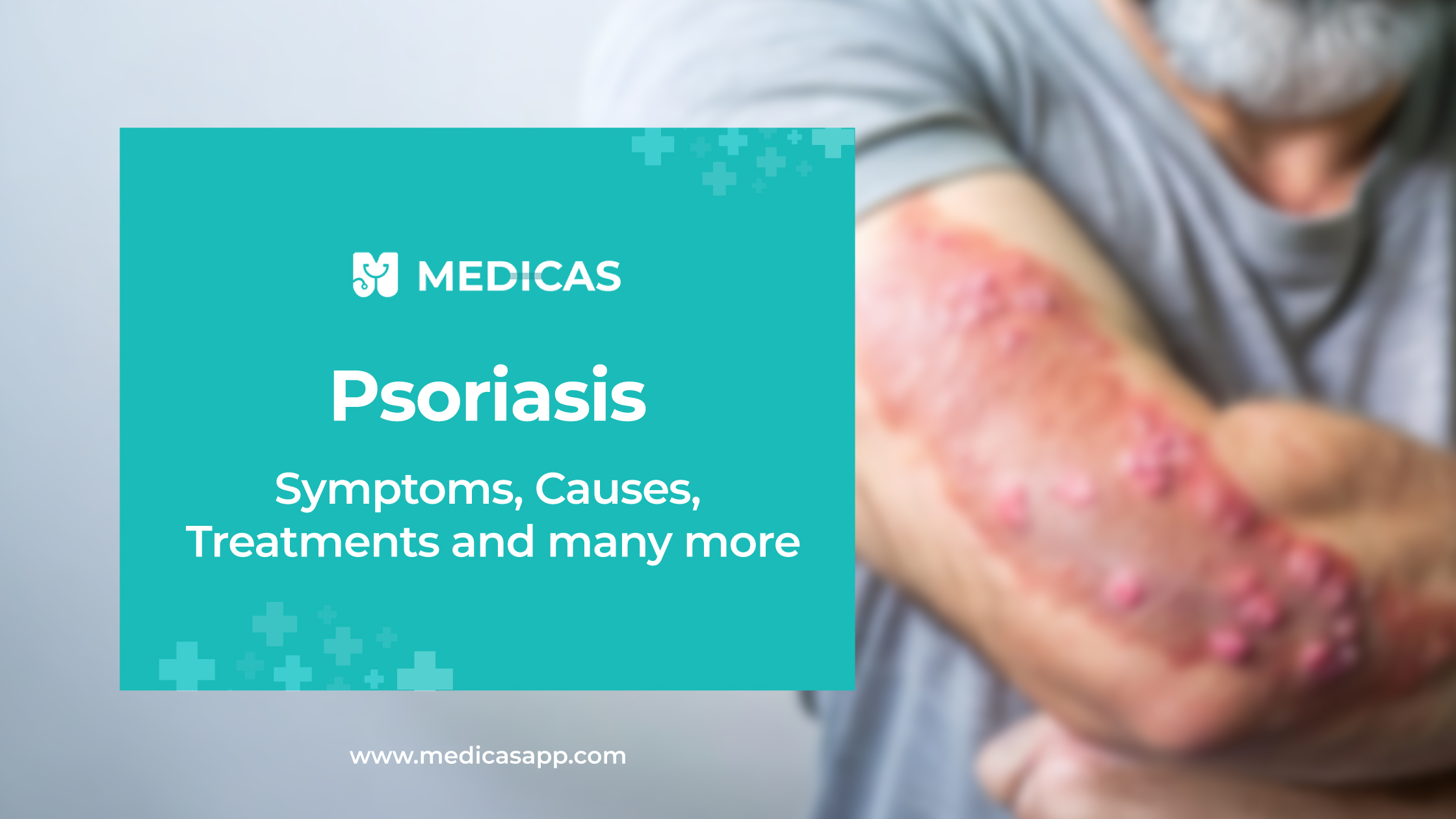
Psoriasis manifests differently in each individual, but some common symptoms include raised, inflamed patches of skin (plaques) covered with silvery scales. These patches often appear on the elbows, knees, scalp, and lower back, but can occur anywhere on the body. Itching, burning, and soreness are frequent complaints. The nails can also be affected, exhibiting pitting, thickening, or separation from the nail bed. In some cases, individuals may experience joint pain and stiffness, indicative of psoriatic arthritis. Understanding these symptoms helps in early detection and management of psoriasis. Keep in mind that symptoms can flare up and subside over time, and triggers vary from person to person. Recognizing your specific symptoms is a crucial step toward effective treatment.
Major Causes of Psoriasis
Psoriasis is primarily an immune-mediated disease, meaning it’s driven by an overactive immune system. While the exact cause is not fully understood, genetics and environmental factors play significant roles. In individuals with psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly attacks healthy skin cells, accelerating the skin cell growth cycle. This overproduction of new skin cells leads to the characteristic buildup of plaques. Genetic predisposition is a key factor, as psoriasis tends to run in families. Environmental triggers, such as stress, infections, skin injuries, and certain medications, can also exacerbate the condition. It’s not contagious, but understanding the interplay between genetics and triggers is vital for managing psoriasis effectively. Proper diagnosis often requires a thorough examination and sometimes a skin biopsy.
Risks associated with Psoriasis
The risks associated with psoriasis extend beyond the visible skin symptoms. Individuals with psoriasis are at a higher risk for developing other health conditions, including psoriatic arthritis, which causes joint pain and stiffness. Cardiovascular disease, such as heart attack and stroke, is also more common in people with psoriasis. Additionally, there is an increased risk of metabolic syndrome, which includes conditions like obesity, high blood pressure, and abnormal cholesterol levels. Mental health issues, such as depression and anxiety, are also prevalent among those with psoriasis due to the chronic nature of the condition and its impact on self-esteem and social interactions. Early diagnosis and proactive management can mitigate these risks and improve overall health. Regular check-ups and a healthy lifestyle are important for those living with psoriasis.
Stage-Wise Risks of Psoriasis
| Stage | Associated Risks |
|---|---|
| Early Stage | Mild skin irritation, localized plaques, potential for misdiagnosis. |
| Moderate Stage | Widespread plaques, increased itching and discomfort, elevated risk of psoriatic arthritis. |
| Severe Stage | Extensive skin involvement, significant pain and disability, higher risk of cardiovascular disease and metabolic syndrome. |
Diagnosis of Psoriasis
Diagnosing psoriasis typically involves a physical examination of the skin, scalp, and nails by a dermatologist. The characteristic appearance of psoriatic plaques is often sufficient for diagnosis. In some cases, a skin biopsy may be performed to rule out other skin conditions or confirm the diagnosis. During a biopsy, a small sample of skin is removed and examined under a microscope. The dermatologist will also inquire about your medical history, family history of psoriasis, and any potential triggers. Distinguishing psoriasis from other skin conditions, such as eczema or fungal infections, is crucial for appropriate treatment. Early and accurate diagnosis is essential for effective management of psoriasis and prevention of complications. Consider using Book Lab Test services for precise analysis.
Prevention of Psoriasis
While there’s no way to completely prevent psoriasis, certain lifestyle modifications and preventive measures can help reduce the frequency and severity of flare-ups. Identifying and avoiding triggers is key. Common triggers include stress, infections, skin injuries, and certain medications. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle through regular exercise, a balanced diet, and adequate sleep can also support immune function and reduce inflammation. Keeping the skin moisturized with emollients can help prevent dryness and cracking, which can trigger flare-ups. Protecting the skin from injury and infection is also important. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as yoga or meditation, can be beneficial. By adopting these preventive strategies, individuals with psoriasis can minimize the impact of the condition on their daily lives. Remember, consistency is key in preventing flare-ups.
Common Treatment Options for Psoriasis
Treatment for psoriasis aims to reduce inflammation, control skin cell turnover, and alleviate symptoms such as itching and scaling. Treatment options vary depending on the severity and location of the psoriasis. Topical treatments, such as corticosteroids, vitamin D analogs, and retinoids, are often the first line of defense for mild to moderate psoriasis. Phototherapy, or light therapy, involves exposing the skin to controlled amounts of ultraviolet light. Systemic medications, such as oral or injectable drugs, are used for more severe cases or when other treatments are ineffective. Biologic drugs, which target specific parts of the immune system, are a newer class of systemic medications. The choice of treatment depends on individual factors, such as the type and severity of psoriasis, overall health, and personal preferences. Consulting with a dermatologist is essential for developing a personalized treatment plan. Now, let’s discuss lifestyle modifications and medications to better understand your treatment options. With Medicas, you can consult a doctor instantly.
Lifestyle Modifications for Psoriasis
Lifestyle modifications play a crucial role in managing psoriasis. These changes can significantly impact the severity and frequency of flare-ups. Regular moisturizing is essential to keep the skin hydrated and prevent dryness, which can trigger psoriasis. Avoiding known triggers, such as certain foods or allergens, can also help reduce flare-ups. A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, and whole grains can support overall health and immune function. Managing stress through relaxation techniques, such as meditation or yoga, can help reduce inflammation. Quitting smoking and limiting alcohol consumption are also important, as these habits can worsen psoriasis. Incorporating these lifestyle modifications into your daily routine can improve your quality of life and complement medical treatments. They’re a simple, yet effective way to take control of your psoriasis.
Medications for Psoriasis
Medications are a cornerstone of psoriasis treatment, and they come in various forms. Topical corticosteroids are often the first line of defense for mild to moderate psoriasis. Vitamin D analogs, such as calcipotriene, help slow down skin cell growth. Retinoids, such as tazarotene, can reduce inflammation and promote skin cell turnover. For more severe cases, systemic medications, such as methotrexate, cyclosporine, and apremilast, may be prescribed. Biologic drugs, such as adalimumab, etanercept, and infliximab, target specific parts of the immune system and can be highly effective. Each medication has its own set of benefits and risks, so it’s important to discuss the options with your doctor. They will consider your specific condition, medical history, and personal preferences when recommending a treatment plan. Remember, finding the right medication may involve some trial and error, but it’s worth it for improved symptom control.
When to See the Doctor for Psoriasis
It’s important to see a doctor if you suspect you have psoriasis or if your symptoms are not well-controlled with over-the-counter treatments. Early diagnosis and treatment can help prevent complications and improve your quality of life. Schedule an appointment with a dermatologist if you experience persistent skin irritation, red or scaly patches, itching, or nail changes. Seek medical attention if you develop joint pain or stiffness, which could indicate psoriatic arthritis. It’s also important to see a doctor if your psoriasis is affecting your ability to perform daily activities or if it’s causing significant emotional distress. Don’t hesitate to seek professional help – a dermatologist can provide an accurate diagnosis and develop a personalized treatment plan tailored to your needs. Your skin health is important, and seeking timely medical care can make a significant difference.
Things to Consider During Treatment/Procedure of Psoriasis
During psoriasis treatment, there are several factors to keep in mind to ensure the best possible outcome. First, adherence to the prescribed treatment plan is crucial. Consistency is key, whether you’re using topical medications, undergoing phototherapy, or taking systemic drugs. Communicate openly with your doctor about any side effects or concerns you may have. They can adjust your treatment plan as needed to minimize side effects and maximize effectiveness. Be patient – it may take time to find the right treatment regimen that works for you. Protect your skin from sun exposure, as some treatments can increase sensitivity to sunlight. Maintain a healthy lifestyle, including a balanced diet, regular exercise, and stress management, to support your overall well-being. By actively participating in your treatment and communicating effectively with your doctor, you can achieve better control over your psoriasis and improve your quality of life.
Related Articles
Disclaimer
The Medicas Health Library provides general health information for educational purposes only. It is not a substitute for professional medical advice, diagnosis, or treatment. Always seek the guidance of a qualified healthcare provider with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition or treatment. While we strive to keep content accurate and up to date, medical knowledge is constantly evolving, and individual circumstances may vary. Medicas does not assume responsibility for decisions made based on this information.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
-
What is psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic, autoimmune skin condition that causes raised, red, scaly patches to appear on the skin.
-
Is psoriasis contagious?
No, psoriasis is not contagious. It is an immune-mediated condition and cannot be spread from person to person.
-
What are the common triggers for psoriasis flare-ups?
Common triggers include stress, infections, skin injuries, certain medications, and cold weather.
-
Can psoriasis be cured?
There is no cure for psoriasis, but various treatments can effectively manage symptoms and improve quality of life.
-
What are the different types of psoriasis?
The main types include plaque psoriasis, guttate psoriasis, inverse psoriasis, pustular psoriasis, and erythrodermic psoriasis.
-
How is psoriasis diagnosed?
Psoriasis is usually diagnosed through a physical examination of the skin, scalp, and nails by a dermatologist. A skin biopsy may be performed in some cases.
-
What are the common treatment options for psoriasis?
Common treatment options include topical medications, phototherapy, systemic medications, and biologic drugs.
-
What is psoriatic arthritis?
Psoriatic arthritis is a type of arthritis that affects some people with psoriasis, causing joint pain, stiffness, and swelling.
-
Can lifestyle modifications help manage psoriasis?
Yes, lifestyle modifications such as moisturizing, avoiding triggers, and managing stress can help manage psoriasis symptoms.
-
Are there any natural remedies for psoriasis?
Some natural remedies, such as aloe vera and Dead Sea salts, may provide relief from psoriasis symptoms, but it’s important to discuss them with your doctor first.
-
How can I protect my skin if I have psoriasis?
Protect your skin by moisturizing regularly, avoiding harsh soaps, and protecting it from injury and sun exposure.
-
Can psoriasis affect my nails?
Yes, psoriasis can affect the nails, causing pitting, thickening, or separation from the nail bed.
-
Is psoriasis linked to other health conditions?
Yes, psoriasis is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular disease, metabolic syndrome, and mental health issues.
-
How often should I see a dermatologist if I have psoriasis?
The frequency of visits depends on the severity of your psoriasis and your treatment plan, but regular check-ups are important for monitoring and managing the condition.
-
Where can I seek help if I have psoriasis?
You can seek help from dermatologists, support groups, and online resources. Don’t hesitate to reach out to your local Book Appointment now to connect with trusted healthcare professionals.